Fichier:Giant iceberg breaks off Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica ESA23184247.gif

Fichier d’origine (1 730 × 1 730 pixels, taille du fichier : 5,32 Mio, type MIME : image/gif, en boucle, 2 trames, 2,0 s)
Ce fichier et sa description proviennent de Wikimedia Commons.
Description
| DescriptionGiant iceberg breaks off Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica ESA23184247.gif |
English: A giant iceberg, approximately 1.5 times the size of Greater Paris, broke off from the northern section of Antarctica’s Brunt Ice Shelf on Friday 26th February. New radar images, captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission, show the 1270 sq km iceberg breaking free and moving away rapidly from the floating ice shelf. Glaciologists have been closely monitoring the many cracks and chasms that have formed in the 150 m thick Brunt Ice Shelf over the past years. In late-2019, a new crack was spotted in the portion of the ice shelf north of the McDonald Ice Rumples, heading towards another large crack near the Stancomb-Wills Glacier Tongue. This latest rift was closely monitored by satellite imagery, as it was seen quickly cutting across the ice shelf. Recent ice surface velocity data derived from Sentinel-1 data indicated the region north of the new crack to be the most unstable – moving around 5 m per day. Then, in the early hours of Friday 26th, the newer crack widened rapidly before finally breaking free from the rest of the floating ice shelf. ESA’s Mark Drinkwater said, “Although the calving of the new berg was expected and forecasted some weeks ago, watching such remote events unfold is still captivating. Over the following weeks and months, the iceberg could be entrained in the swift south-westerly flowing coastal current, run aground or cause further damage by bumping into the southern Brunt Ice Shelf. So we will be carefully monitoring the situation using data provided by the Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission.” Although currently unnamed, the iceberg has been informally dubbed ‘A-74’. Antarctic icebergs are named from the Antarctic quadrant in which they were originally sighted, then a sequential number, then, if the iceberg breaks, a sequential letter. The calving does not pose a threat to the presently unmanned British Antarctic Survey’s Halley VI Research Station, which was re-positioned in 2017 to a more secure location after the ice shelf was deemed unsafe. Routine monitoring by satellites offer unprecedented views of events happening in remote regions like Antarctica, and how ice shelves manage to retain their structural integrity in response to changes in ice dynamics, air and ocean temperatures. The Copernicus Sentinel-1 mission carries radar, which can return images regardless of day or night and this allows us year-round viewing, which is especially important through the long, dark, austral winter months. |
| Date | 2 mars 2021 (date de téléversement) |
| Source | Giant iceberg breaks off Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica |
| Auteur | European Space Agency |
| Activity InfoField | Observing the Earth |
| Mission InfoField | Sentinel-1 |
| System InfoField | Copernicus |
Conditions d’utilisation

|
This image contains data from a satellite in the Copernicus Programme, such as Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 or Sentinel-3. Attribution is required when using this image.
Attribution: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data 2021
Attribution
The use of Copernicus Sentinel Data is regulated under EU law (Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) No 1159/2013 and Regulation (EU) No 377/2014). Relevant excerpts:
Free access shall be given to GMES dedicated data [...] made available through GMES dissemination platforms [...].
Access to GMES dedicated data [...] shall be given for the purpose of the following use in so far as it is lawful:
GMES dedicated data [...] may be used worldwide without limitations in time.
GMES dedicated data and GMES service information are provided to users without any express or implied warranty, including as regards quality and suitability for any purpose. |
Attribution
This media was created by the European Space Agency (ESA).
Where expressly so stated, images or videos are covered by the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 IGO (CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO) licence, ESA being an Intergovernmental Organisation (IGO), as defined by the CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO licence. The user is allowed under the terms and conditions of the CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO license to Reproduce, Distribute and Publicly Perform the ESA images and videos released under CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO licence and the Adaptations thereof, without further explicit permission being necessary, for as long as the user complies with the conditions and restrictions set forth in the CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO licence, these including that:
See the ESA Creative Commons copyright notice for complete information, and this article for additional details.
|
 | |
Ce fichier est soumis à la licence Creative Commons Attribution – Partage dans les Mêmes Conditions 3.0 IGO. Attribution: ESA, CC BY-SA IGO 3.0
| ||
Légendes
Éléments décrits dans ce fichier
dépeint
2 mars 2021
image/gif
Historique du fichier
Cliquer sur une date et heure pour voir le fichier tel qu'il était à ce moment-là.
| Date et heure | Vignette | Dimensions | Utilisateur | Commentaire | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actuel | 2 mars 2021 à 10:55 | 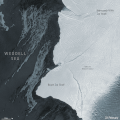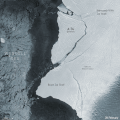 | 1 730 × 1 730 (5,32 Mio) | OptimusPrimeBot | #Spacemedia - Upload of https://www.esa.int/var/esa/storage/images/esa_multimedia/images/2021/03/giant_iceberg_breaks_off_brunt_ice_shelf_in_antarctica/23184237-3-eng-GB/Giant_iceberg_breaks_off_Brunt_Ice_Shelf_in_Antarctica.gif via Commons:Spacemedia |
Utilisation du fichier
Les 2 pages suivantes utilisent ce fichier :
Usage global du fichier
Les autres wikis suivants utilisent ce fichier :
- Utilisation sur de.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur no.wikipedia.org
- Utilisation sur www.wikidata.org
Métadonnées
Ce fichier contient des informations supplémentaires, probablement ajoutées par l'appareil photo numérique ou le numériseur utilisé pour le créer.
Si le fichier a été modifié depuis son état original, certains détails peuvent ne pas refléter entièrement l'image modifiée.
| Identifiant unique du document original | xmp.did:f39ada98-e52a-0d4c-bfbc-ee87326b2e73 |
|---|---|
| Logiciel utilisé | Adobe Photoshop 21.2 (Windows) |

